Top > Technologies > in-situ Illumination Technologies for NMR
In situ illumination of liquid-state NMR samples opens a field for studies of light-dependent chemical or biological interactions. Among those studies, the light-driven reactions between amino acid and dye molecule, studied by photochemical induced nuclear polarization (photo-CIDNP) in solution, have been investigated to show characteristic changes in spin polarization upon various magnetic fields. The applications of photo-CIDNP, such as detecting aromatic amino acids or proteins in solution in the low micro-molar to nano-molar concentration range, are getting compelling simultaneously.
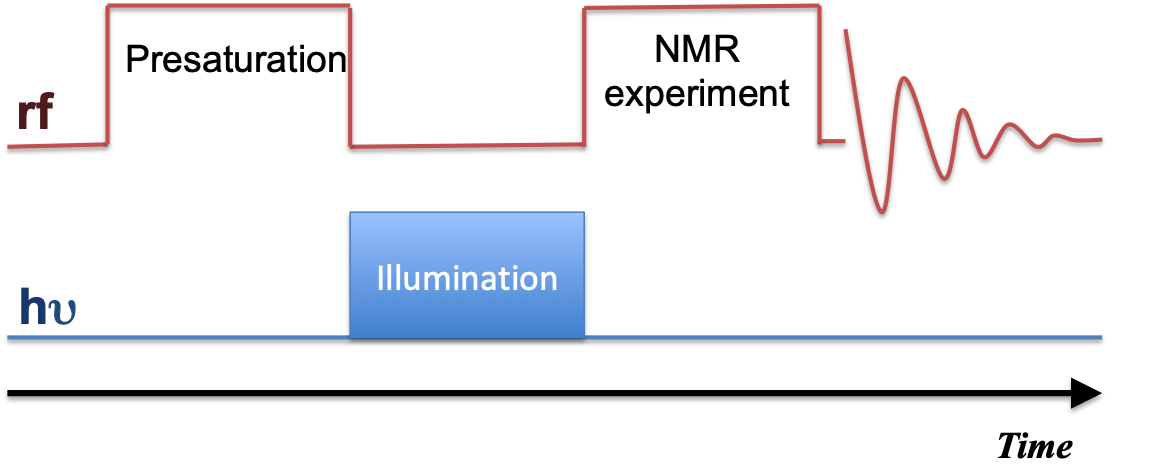
The time sequence shows how to perform the irradiation along with the NMR sequence. For low-field irradiation, the sample travels to the low field for irradiation and shuttles back immediately for pulsing and acquisition.
Due to the narrow bore of most commercial standard liquid-state NMR spectrometers, there was challenging to place a light source directly inside the magnet. Conventionally, the light source and control unit were outside of the spectrometer. The light, from lasers, or LED, was coupled through the long optical fiber to samples. The major drawback of this manner is that the long optical fiber confines the movement of the NMR sample. It would be severe for field-cycling NMR applications. For non-field-cycling studies, light homogeneity is also an issue for light coupling from the long thin optical fiber.
Hence, we have developed compact and high-precision shuttling equipment that shuttles and illuminates the sample at the stray field in a high-field NMR spectrometer to obtain high-resolution spectra containing the effect of field-dependent CIDNP, Field Cycling NMR illuminator. For non-field-cycling NMR users, we have also designed a compact illuminator installed directly on the sample tube, in-situ NMR illuminator.
References
- Siyu Li, Shibani Bhattacharya, Ching-Yu Chou, Minglee Chu, Shu-Cheng Chou, Marco Tonelli, Michael Goger, Hanming Yang, Arthur G. Palmer, Silvia Cavagnero, Journal of Magnetic Resonance 359 (2024) 107616
- Yining Ji, Daniel A. DiRocco, Cynthia M. Hong, Michael K. Wismer, and Mikhail Reibarkh, Organic Letters 2018 20 (8), 2156-2159, DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b00391
- Dan Lehnherr, Yining Ji, Andrew J. Neel, Ryan D. Cohen, Andrew P. J. Brunskill, Junyu Yang, and Mikhail Reibarkh, Journal of the American Chemical Society 2018 140 (42), 13843-13853, DOI: 10.1021/jacs.8b08596
- Fedin, M.V., E.G. Bagryanskaya, and P.A. Purtov, Theoretical and experimental studies of chemically induced dynamic nuclear polarization kinetics in recombination of radical pairs by the method of switched external magnetic field. II. 13C CIDNP of micellized radical pairs. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1999. 111(12): p. 5491-5502.
- Kuhn, L.T., Photo-CIDNP NMR Spectroscopy of Amino Acids and Proteins. 2013. 338: p. 229-300.
- Magin, I.M., et al., Low field photo-CIDNP in the intramolecular electron transfer of naproxen–pyrrolidine dyads. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2016. 18(2): p. 901-907.
- Seegerer, A., P. Nitschke, and R.M. Gschwind, Combined In Situ Illumination-NMR-UV/Vis Spectroscopy: A New Mechanistic Tool in Photochemistry. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018. 57(25): p. 7493-7497.
- Ji, Y., et al., LED‐Illuminated NMR Spectroscopy: A Practical Tool for Mechanistic Studies of Photochemical Reactions. ChemPhotoChem, 2019. 3(10): p. 984-992.
- Grosse, S., et al., Field cycling by fast NMR probe transfer: Design and application in field-dependent CIDNP experiments. Applied Magnetic Resonance, 1999. 17(2): p. 211-225.
- Philipp Nitschke, Nanjundappa Lokesh, Ruth M. Gschwind, Combination of illumination and high resolution NMR spectroscopy: Key features and practical aspects, photochemical applications, and new concepts. Progress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, Volumes 114–115, October–December 2019, Pages 86-134
- Lars T. Kuhn, Míriam Pérez-Trujillo, Continuous-Wave (CW) Photo-CIDNP NMR Spectroscopy: A Tutorial, Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry: 2025. 0:1–15.
